Safe Protocol for Amalgam Removal
International Academy of Oral Medicine and Toxicology (International Academy of Oral Medicine and Toxicology-IAOMT).
Protocol for removal of mercury amalgams / silver (1)
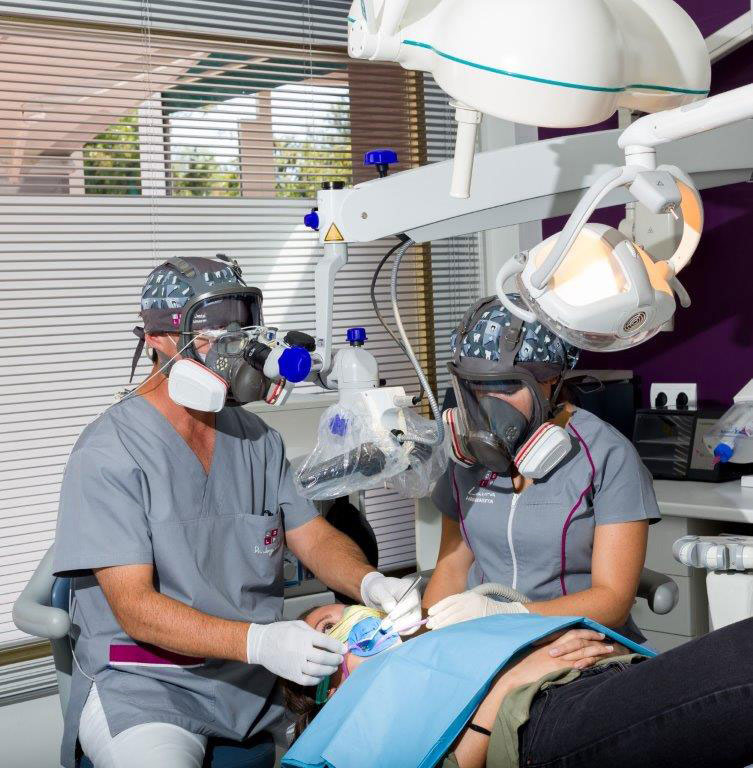
PATIENT PROTECTION
The first, in the mind of all conscious doctor is patient protection against further exposure to mercury. This is especially true in patients with mercury poisoning. The mercury toxic patient may have been exposed to varying amounts of mercury in the diet, in the environment, in the workplace or mercury amalgams / silver. All forms are cumulative and can contribute to the body burden of mercury. The goal of this procedure is to minimize any additional exposure of the patient, ourselves , or staff to mercury. During chewing the patient to intraoral levels which are several times the concentration of mercury in air allowed by the EPA exposed ( 2) (Environmental Protection Agency, orUS Environmental Protection Agency). During the removal or placement of amalgam the patient can be exposed to amounts which are a thousand times greater than allowed by the EPA (3) concentration. Once the drill touches the amalgam temperature increases immediately vaporizing the mercury component of the alloy.
There are 8 steps to greatly reduce the exposure of all people:
- Keep the fillings cool.
All removal must be done under cold water spray with copious amounts of water. Once the removal has begun, the mercury vapor will be continuously released from the tooth.
- Use a high volume evacuator.
A sniffer tip high volume should be kept near the tooth (less than 1 cm. And a half) at all times to evacuate the vapor from the area of the patient. Polishing amalgam can create very dangerous levels of mercury and should be avoided especially for the mercury toxic patient.
- Provide an alternative air source.
All patients that they are an amalgam removed or placed should be provided with an alternative air source and should be instructed to not breathe through your mouth during treatment. A nasal mask such as that used with the anesthesia team nitrous oxide is excellent. Air is best and oxygen is acceptable although not required. If only air is used, it must be clean and free of mercury vapor preferably taken from outside the dental clinic.
- Immediate elimination of mercury alloy.
Particles mercury alloy should be washed and vacuumed as soon as they are generated. The filling should be sectioned and removed in large pieces to reduce exposure. Currently the International Academy of Oral Medicine and Toxicology (IAOMT) has approved the removal without the use of a rubber dam. There is some evidence to support both views since high levels of particulate matter and mercury amalgam can be found below the dam. All members agree that whether or not you use a oral rubber dam should be instructed to not breathe through your mouth and not swallow the particles of amalgam. Some experts feel it is better to remove the amalgam first and then apply the dam if needed for restorative procedures.
- Washing and changing of gloves.
After the fillings have been removed, take out the rubber dam if it was used and make a patient mouth wash for at least 30 seconds with cold water and suction. Take off your gloves and replace them with a new pair. If then you are making a restorative procedure then reapply a new dam and proceed.
- Clean the patient immediately.
Immediately change patient protective wear and clean their face.
- Consider food aid.
Consider appropriate nutritional support before, during and after removal. [MERCURIADOS Note: Please note that this is a literal translation. We are in contact with the directors of the International Academy of Oral Medicine and Toxicology, with "food aid" does not refer at all to eat but to take chlorella or selenium, p. eg. Some even advised to take much cilantro months before removing the mercurial source. In that case, there is a risk (does not mean you have to spend) redistribution of mercury. What to drink plenty of water or milk (or liquid yogurt) the day of removal is the most common and less complicated. Proper removal of amalgams is always useful, but be tb. into account that he is not allergic to mercury, have their kidney function working well or fairly well (just do the test Creatinine clearance) and their overall health is not very damaged, they do not have to have a greater problem with withdrawals fairly adequate or even unprotected (unless increasingly many amalgams are removed and / or other circumstances)].
- Keep the air clean room.
Install air purifiers or ionizers and fans for the welfare of everyone.
PERSONAL PROTECTION
OSHA (4) (5) (Occupational Safety & Health Administration, equivalent to the Ministry of Labour and Spanish Social Affairs) requires employees to give an informed written consent before the use of any toxic chemicals of which mercury is one. Elemental mercury vapor is one of the most toxic forms of mercury and should not be inhaled. Women of childbearing age should not be exposed to more than 10% of the OSHA MAC (6) (MAC = Mexican-American Commission or Commission Mejicana-North America). Women who are pregnant should not be exposed to mercury (7). If you use mercury or remove mercury in any form, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has recommended that medically supervise their employees annually.
ANY EXPOSURE TO MERCURY requires the employee to wear a mask APPROVED WITH MERCURY FILTER.
An approved mask is appropriate for wearing during all dental procedures that expose you or your staff to mercury (8). The way in which dentists operate their equipment dramatically affects the amount of mercury ejected. Never drill mercury dry. It is dangerous for you, your staff, and your patient. Levels have been measured up to 4000 mg / m3 to half a meter drill when used dry. They have measured levels above 1000 mg / m3 when opening an amalgam mixing capsule. One out of 7 California dental clinics tested by OSHA mercury contamination showed 50 mg / m3. In 100% of clinics, he gave vacuum extractor levels above 100 mg / m3. Any clinic where mercury is used should be monitored regularly and should monitor personnel exposure. Testing services are available and a mercury sensor is available for staff supervision. It must be checked within warehouses and along surfaces where mercury may have fallen. Spills in the clinic may go unnoticed for years and are extremely dangerous.
DENTAL CLINIC PALM TREES
We've Add:
- Always isolate with rubber dam u optradame
-Filters Gold to protect the patient against mercury vapors
-Filters Against mercury vapors for auxiliary and Dres
-Filters For metals in suction systems dental chairs to protect the environment
-We Use amplification systems (Lupas and Omni Peak Zeiss Microscope).

